What are the used path of HTTP request generated by your web browser to load a web page between your computer and a server web? I suppose each time DNS resolution is done, that is to say the web browser knows IP server.
Internet is a network of routers. When your web browser is sending one HTTP request your computer uses by default the destination 0.0.0.0 if no one sub-network matches with your original destination IP address in its route table.
$ route -n
Destination Gateway Genmask Flags Metric Ref Use Iface
0.0.0.0 192.168.1.254 0.0.0.0 UG 600 0 0 wlp6s0
Here the gateway 192.168.1.254 is my Internet box related to network interface wlp6s0.
$ nslookup 192.168.1.254
Server: 127.0.1.1
Address: 127.0.1.1#53
name = bbox.lan.
Your request is sent to box of your Internet Service Provider (ISP), for me it is a French ISP: Bouygues Telecom. Leaving your Local Area Network (LAN) to the Wide Area Network (WAN) of Internet, thanks to Network Address Translation (NAT), your box replaces IP address source in the header of your HTTP request (equals to your private IP, see ifconfig wlp6s0) by its public IP address (see dig +short myip.opendns.com @resolver1.opendns.com), and keeps in memory this matching only for this request in order to it comes from your computer by doing reverse translation.
The Time to live (TTL) of your request allows to know how many maximally your request can cross routers before arriving at destination. It prevents infinite cycle of routers in the network, by default a value of 64 is recommended depending of diameter of Internet. By modifying this value from 1 to N, you can get the IP address of each router on the path of your request: it will be the IP source of the response of your request HTTP.
For example, you can get TTL minimum by successive ping commands, see details in n_routers.sh bash script. Each router must decrement TTL value and if TTL is 0, it refuses to transmit message. The minimum TTL is length path in the network to reach the server (by excluding source machine for number of nodes or is directly number of edges). Here one time to live of 4 is insufficient to reach glegoux.com from my machine location:
$ ping -c 1 -t 4 glegoux.com
PING glegoux.com (195.164.48.181) 56(84) bytes of data.
From 10.125.135.205 icmp_seq=1 Time to live exceeded
--- glegoux.com ping statistics ---
1 packets transmitted, 0 received, +1 errors, 100% packet loss, time 0ms
This is valid for outward network path your TTL must be sufficient, you can see your current TTL cat /proc/sys/net/ipv4/ip_default_ttl or with ping -c 1 localhost (for Linux default value is 64), and change that without persistence sudo sysctl net.ipv4.ip_default_ttl=128. Targeted server must have also sufficient TTL for return network path, this value is decremented (until value 56 here, but we don’t know initial value a priori):
$ ping -c 1 glegoux.com
PING glegoux.com (195.164.48.181) 56(84) bytes of data.
64 bytes from 10.125.135.205.rev.poneytelecom.eu (10.125.135.205): icmp_seq=1 ttl=56 time=13.8 ms
--- glegoux.com ping statistics ---
1 packets transmitted, 1 received, 0% packet loss, time 0ms
rtt min/avg/max/mdev = 13.821/13.821/13.821/0.000 ms
While ping command uses ICMP protocol, the system command traceroute realizes that directly with TCP protocol more easily. If there are stars instead of one IP address it means router refused to give its identity.
There is no rule to guarantee that outward path and return path are identical. This is sometimes useful to get traceroute from both ends of your network. Here I am considering only outward path.
By combining that with free IP locator like :
You can locate request path via Application Programming Interface (API) with the usage of pre-computed databases of geolocalisation of these free IP locators.
It is important to keep in mind that IP locator is not 100% accurate, only 95% for the best ones. And behind one IP address can hide a web proxy and a virtual private cluster preventing to locate really the destination. Thanks to Regional Internet Registry (RIR) and static address IP of ISPs, IP locators can know the location of some IP addresses easily.
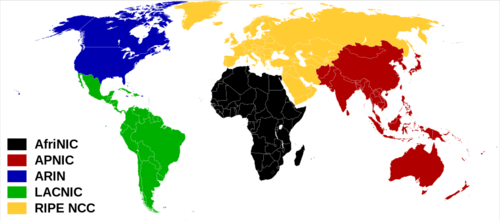
But an constant update and smart analysis of the network is required to locate any IP address (IPv4 or IPv6), because of dynamic IP addresses and moving connected objects for instance in the Internet of Things (IoT) or mobile networks. In addition, this location could not be too precised to respect private life of each Internet surfer, even if this one shares its location via its web browser.
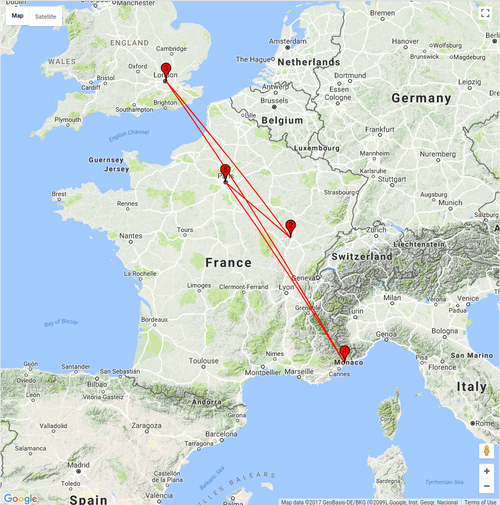
With this Proof of Concept (PoC), you can run get_route.sh glegoux.com to get IP locations in csv file route.csv and see the result via Google Maps (just get your own API token) and a python web server by executing httpserver.sh and by visualizing index.html in your favorite web browser.




Comments